Precision PCB Fabrication, PCB Assembly, DIP Assembly, BGA Assembly etc..
We provide the most competitive PCB & PCBA services.
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search












An excellent hardware engineer, in addition to strong basic theoretical knowledge, proficient in hardware schematic design technology, hardware PCB diagram design, and hardware debugging, must also have the ability to learn quickly, understand communication protocols and standards, and have the ability to design circuits. , communication and overall control ability, material selection ability, procurement ability, etc., even from the engineering theoretical and economic situation, down to the history, politics, culture and technology, you must understand a little...
Level zero:
1. Knowledge of basic technology;
2. The electromagnetic basis of analog electricity, digital electricity, circuit analysis, signal and system, physics;
3. Basic knowledge of welding, circuit design software, use of oscilloscope, multimeter and other basic instruments.
Level one:
1. Energy is mainly spent on learning schematic tools and PCB tools;
2. The main concern is that the PCB line can go through or not, it is more nervous, and it is afraid of connecting the wrong line;
3. For circuit principles, there is no time and energy to pay attention to. Generally, mainly copy other people's circuits, and prefer books with case circuits;
4. About PCB, the main concern is whether the line can be connected or not. There is no clear concept of signal integrity and the length and width of the trace.
Level two:
1. The schematic diagram and PCB tools have been skilled operation;
2. Begin to pay attention to the circuit principle and the influence of the device's index on the circuit operation;
3. Allocate energy to study the Datasheet of components;
4. Pay attention to the difference between different types of discrete devices. When selecting devices, you can think independently. You can use any circuit instead of what circuit you can copy.
Level three:
Able to design solutions and solve problems. Proficient in high-speed digital circuits, radio frequency, FPGA, large-scale circuit design (such as X86, etc.) EMC and other skills.
1. The risk of the circuit can be controlled, and some problems that may affect the function will be considered in the schematic diagram and device selection, instead of solving the problem when the circuit is back to the board for debugging;
2. When designing the circuit, consider the tolerance design and the imperfection of the device, such as the change with temperature, the influence of accuracy, and the influence of voltage;
3. In PCB design, in addition to line connectivity, the impact of high speed, radio frequency, and high current on circuit performance is also considered. Ability to analyze signal timing and impedance continuity;
4. Solve signal integrity problems by means of analysis or simulation tools.
Level four:
Be able to design stable and reliable products that meet industry standards and support mass-delivery products.
1. Able to consider dimensions other than functionality: low cost, easy to process, easy to purchase, easy to test, easy to diagnose problems online, not easily damaged by transportation or vibration, easy to repair, easy to maintain;
2. The designed products can meet the needs of high reliability;
3. Be able to innovate and make innovative products based on existing circuits or solutions; or be able to achieve technological advancement in a certain technical field, and the products made have technical breaking points. Be able to apply for patents with practical value to effectively protect the innovation of their products;
4. Able to design products that support mass delivery;
5. Able to control the development and operation of super-large hardware systems.
Level five:
Be able to formulate some standards, specifications, patents, etc. to form industry benchmarks, or be innovative.
1. With industry thinking, you can take into account the needs of application scenarios and macroscopically consider market trends and trends before project approval.
2. Be able to predict the entire life cycle of the product, and be able to comprehensively consider product design, cost control, product positioning, and full-cycle human input allocation from technology implementation, project management, supply chain, and market demand.
3. It can get through the upstream and downstream, and can control the suppliers and distributors.
Level six:
It has social influence and influences the industry ecology.
1. Have the ability to deliver high-quality products, have a complete knowledge system, have complete delivery capabilities and experience of more complex hardware products, fully grasp the hardware R&D process, and have a good understanding of reliability, maintainability, testability, producibility, In-depth understanding and practical experience of availability;
2. Ability to tackle key problems, have a rigorous attitude towards problems, and problem analysis ability, strong logical thinking ability;
3. The basic theories such as mathematical physics are solid, and the problem can be analyzed theoretically, not empirical;
4. Industrial vision, global vision, can quickly grasp the rules of industrial trends, new chips, new technologies, and new fields, and have a keen sense of smell.
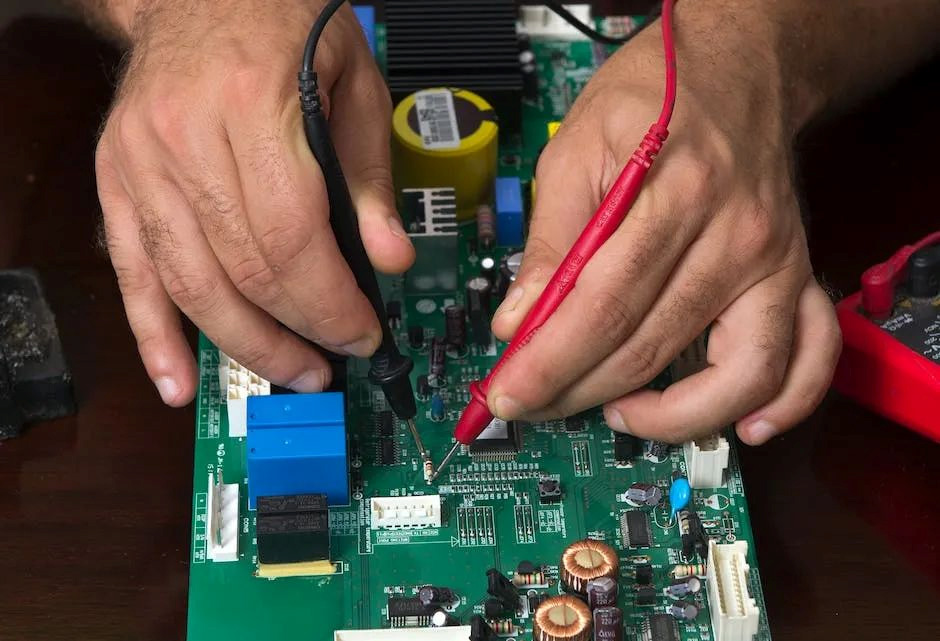
Hardware engineers play a very important role in the entire R&D team. They not only need to communicate with the outside world to obtain requirements for their own designs, and then summarize and analyze them into specific hardware implementations, but also contact many chip and solution suppliers to select them, choose the right solution from them.
When the schematic diagram is completed, it is necessary to organize personnel to cooperate with the review and inspection, and work with the CAD engineer to complete the design. At the same time, prepare the BOM list, start purchasing and preparing materials, and contact the processing manufacturer to complete the placement process.
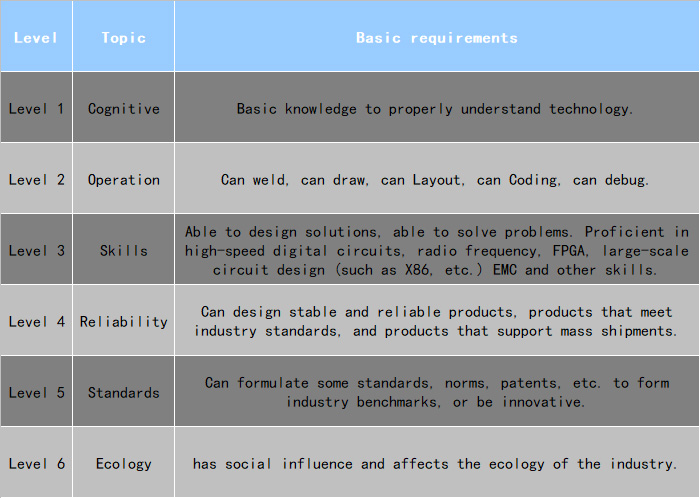
Level 1, Cognitive: Basic knowledge to properly understand technology.
Level2, Operation: can weld, can draw, can Layout, can Coding, can debug.
Level 3, Skills: able to design solutions, able to solve problems. Proficient in high-speed digital circuits, radio frequency, FPGA, large-scale circuit design (such as X86, etc.) EMC and other skills.
Level 4, Reliability: can design stable and reliable products, products that meet industry standards, and products that support mass shipments.
Level 5, Standards: can formulate some standards, norms, patents, etc. to form industry benchmarks, or be innovative.
Level 6, Ecology: has social influence and affects the ecology of the industry.
In short, hardware engineers need experience and need many years of experience to reach a relatively high level. So don't be too lofty, down-to-earth, accumulation is the king!